· weight loss · 7 min read
HOW TO LOSE WEIGHT WITHOUT LOSING MUSCLE: THE ULTIMATE 2024 GUIDE
As someone who has struggled with my weight for years, I know how frustrating and demoralizing it can be to lose weight, only to realize you've also lost precious muscle mass in the process
As someone who has struggled with my weight for years, I know how frustrating and demoralizing it can be to lose weight, only to realize you’ve also lost precious muscle mass in the process. Achieving a lean, toned physique isn’t just about shedding pounds – it’s about burning fat while preserving and even building metabolic muscle. That’s why I’ve put together this comprehensive guide on how to lose weight without losing muscle in 2024.
Too often, people focus solely on the number on the scale, but true progress lies in improving your body composition by decreasing fat while maintaining or increasing lean muscle tissue. Not only does preserving muscle create a more aesthetic, sculpted look, but it also boosts your metabolism, preventing the dreaded “skinny-fat” appearance that plagues many chronic dieters.
In this guide, I’ll take you through every key element required to successfully lose weight while holding onto your hard-earned muscle. We’ll cover optimal nutrition strategies, tailored strength training protocols, cardio recommendations, and important lifestyle factors – all geared towards maximizing fat loss while sending the right signals to your body to maintain and even build lean mass.
But before we dive into the specifics, it’s crucial to understand the fundamental differences between weight loss, fat loss, and muscle loss. Many people use these terms interchangeably, but they are distinct concepts with varying impacts on your overall body composition and health…
Nutrition for Preserving Muscle While Losing Weight
At the core of any successful fat loss and muscle preservation plan lies a properly structured nutrition program. While creating a calorie deficit is necessary for weight loss, going too low in calories or failing to meet your body’s protein and nutrient needs can sabotage your efforts to maintain muscle.
The first step is to calculate your calorie and macronutrient needs for a moderate calorie deficit of around 200-500 calories below your maintenance level. This controlled deficit will allow you to lose fat gradually without risking excessive muscle loss. Online calculators and working with a professional can help determine your ideal intake.
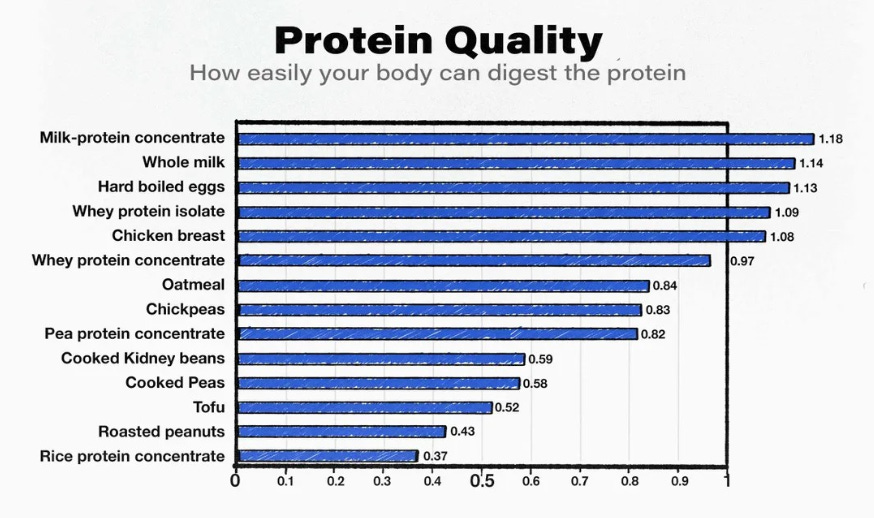
Protein intake is crucial for preserving lean body mass. I recommend consuming 0.6-0.8 grams of protein per pound of body weight from high-quality sources like lean meats, eggs, fish, Greek yogurt and plant-based proteins. Spacing this out over 4-6 meals can further maximize muscle protein synthesis.
Carbohydrates and healthy fats also play important roles. A moderate carb intake ranging from 0.5-2 grams per pound of body weight can help fuel your training sessions while preserving glycogen stores in the muscle. Healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, olive oil and fatty fish help optimize hormone levels.
Finally, pay attention to nutrient timing, especially around your workouts. Consuming a mix of fast-digesting protein and carbs before lifting and a slower-digesting protein source after can help support muscle recovery and growth.
Strength Training for Fat Loss and Muscle Preservation
While nutrition lays the foundation, properly programmed strength training is essential for sending the powerful muscle-preserving signal to your body while dieting. Lifting weights triggers mechanisms that “tell” your body to hold onto its metabolically active lean mass.
I recommend scheduling 3-5 full-body or upper/lower body split resistance training sessions per week, allowing for proper recovery between sessions. Focus on compound lifts like squats, deadlifts, presses and rows that work multiple muscle groups. Progressive overload by gradually increasing weight, reps or intensity over time is key for continual muscle-building stimulus.
Your workouts can include higher rep ranges of 8-15 reps for maintaining muscle, while lower rep ranges of 4-8 reps can facilitate strength and muscle growth if you’re looking to build as you lose fat. Vary your rep schemes, intensities and exercise variations to continually challenge your muscles.
Sample muscle-preserving strength training routines could include an upper body push/pull split, alternating between compound pressing and rowing movements paired with accessory arm and shoulder work. Lower body days can focus on squats or deadlift variations combined with supplementary single-leg movements for the glutes and hamstrings.
Cardio for Fat Burning Without Muscle Loss
While strength training provides the prime muscle-preserving signal, incorporating cardio can help amplify your calorie deficit for increased fat loss. However, the type, amount and timing of cardio are important factors to consider.
Low-intensity steady-state (LISS) cardio like walking, cycling or light jogging is generally better tolerated when dieting compared to high-intensity interval training (HIIT) which can be more stressful when combined with weightlifting in a calorie deficit.
I suggest starting with 2-4 LISS cardio sessions of 30-60 minutes per week, carefully monitoring how your body responds in terms of recovery, hunger levels and muscle fullness. HIIT can be used sparingly, such as 1-2 sessions per week separate from your lifting days.
It’s also important not to overdo cardio, as excessive volumes can impair strength performance and potentially contribute to muscle loss over time. Be aware of potential signs you may be overdoing it like energy lags, poor recovery between sessions and prolonged excessive hunger.
The ideal strategy is to use the minimal effective dose of cardio to accelerate fat loss while allowing your nutrition and strength training to take priority for preserving muscle.
Other Lifestyle Factors for Optimizing Body Recomposition
In addition to your training and nutrition, several other lifestyle factors can play a role in maximizing fat loss while preserving lean mass:
Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours per night to allow your body to properly recover, regulate appetite hormones and optimize muscle protein synthesis. Lack of quality sleep can disrupt this process.
Stress Management: High stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels which may contribute to muscle breakdown over time. Practice stress relief techniques like meditation, deep breathing and schedule “de-load” weeks.
Hydration: Adequate water intake improves recovery, nutrient transportation and can help reduce water retention and bloating when dieting.
Light Activity: Incorporate light movement like walking outside of dedicated exercise sessions to increase your daily energy expenditure without overly taxing your body.
Supplementation: While not required, supplements like whey protein, creatine and ZMA can provide marginal benefits for maintaining lean mass when combined with proper training and nutrition.
Perhaps most importantly, be patient and stay consistent. Transforming your body composition is a gradual process that cannot be rushed. By integrating all these elements into your lifestyle, you’ll be well on your way to losing fat, preserving hard-earned muscle and achieving the strong, lean, sculpted physique you desire.
Conclusion
Losing weight without sacrificing your hard-earned muscle is absolutely achievable, but it requires a strategic, multi-pronged approach. Throughout this guide, I’ve aimed to provide you with a comprehensive game plan that brings together precise nutrition, intelligent strength training, properly programmed cardio, and essential lifestyle factors.
At the core is dialing in a moderate calorie deficit through tailored macro targets, emphasizing adequate protein intake to preserve lean mass and fuel your training sessions. Combining this with a focused resistance training routine centered around compound lifts and progressive overload will send the powerful signal to your body to maintain and even build muscle as you shed fat.
Supplementing your strength work with an appropriate dose of lower-intensity steady-state cardio can accelerate fat loss when needed. But be cautious of overdoing more strenuous cardio which can start to work against your muscle preservation efforts.
Maximizing other habits like quality sleep, stress management, proper hydration and active recovery days will help create an ideal internal environment for your body to prioritize maintaining muscle while releasing stubborn fat stores.
While logistically simple, I can’t overstate that this process takes tremendous patience, discipline and consistency. Results won’t happen overnight, but by integrating this multi-layered approach into your lifestyle, you can achieve that lean, sculpted, athletic physique you’ve always desired.
The path to becoming leaner, more defined and more metabolically robust doesn’t require losing hard-earned muscle mass. By making your training, nutrition and recovery as muscle-focused as possible while in a controlled calorie deficit, you can effectively burn fat while preserving and even building metabolic lean mass.
Stay the course, trust the process, and you’ll have the tools to transform your body composition in a way that accentuates your hard work and discipline. Here’s to losing weight the smart way in 2024 while looking better, performing better and functioning at your absolute best.